Describe Batholiths and Explain Where and How They Form
Earths Dynamic Systems The formation of the Sierra Nevada Mountains can explain the massive exposures of batholiths. Laccoliths are lens-shaped and normally 12 km at the thickest.

Batholith Geology Characteristics Formation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Intrusive volcanism is a type of activity where magma is forced into the rocks that make up the crust of the Earth and when with time it cools and later becomes solid but still remains underground this leads to the formation of different features such as plutons.

. Batholith comes from Greek culture. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock-types such as granite quartz monzonite or diorite see also granite dome. It is generally a dark grey coloured rock.
How Do Plate Tectonics Explain The Formation Of Metamorphic Rocks. Batholiths in particular are the largest and most complex of these plutonic formations. Metamorphic rocks result from the forces active during plate tectonic processesThe tectonic forces deform and break the rock creating openings cracks faults breccias and zones of weakness along which magmas can rise.
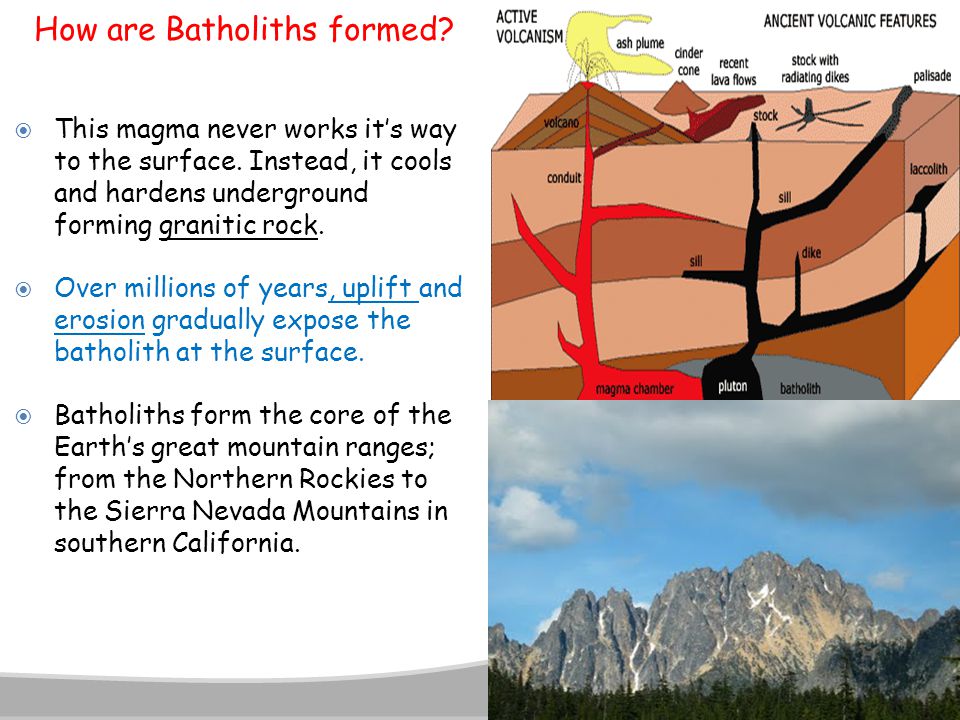
An example of this is the Sierra Nevada Batholith in eastern California see photo below. Batho means depth and litho is rock. Batholiths are typically formed when a number of stocks coalesce beneath the surface to create one large body.
Describe two ways in which batholiths intrude into existing rock. That pluton magmas rise in detached balloonlike forms through the crust frequently reach ing the earths surface and coalesce into shallow and fairly thin complexes. These are large granitic rock bodies formed due to solidification of hot magma inside the earth.
The maximum of batholiths is made of felsic or intermediate rock types like quartz monzonite granite or diorite. They are the result of many many surges over long periods of time all frustrated and subjected to the same burial only to share their eventual resurrection. Batholiths form from magmas generated in the upper mantle and lower crust beneath any depths exposed by erosion.
Usually these rocks are a formation of cooled magma deep in the Earths crust. Batholiths are large masses of intrusive igneous rock that form and cool deep in the Earths crust and this quizworksheet combo will help you understand them better. They form when the stiff cold rock above a magma chamber cannot be supported and collapses to create a broad bowl- like depression.
Batholiths form in mountain belts and can only be exposed through numerous sequences of uplift and erosion. Many batholiths cover hundreds to thousands of square miles. Obsidian is likely felsic.
These form at mid-ocean ridges and act as feeders to the overlying lava flows that erupt in the axial rift valley. Landscape Evolution in the United States 2013. Batholiths form the core of huge mountains and may be exposed on the surface after erosion.
By definition a batholith must cover at least 39 mi 2 100 km 2 although most are even larger. Fissure eruptions produce massive floods of low- viscosity silica- poor lava from large cracks in the crust. They are formed from the hot lava that erupts from the volcano onto the surface of the Earth.
It is generally a dark coloured rock. As concordant bodies laccoliths and lopoliths are variants of sills. Intrusive rocks are characterized by large crystal sizes and as the individual crystals are visible the rock is called phaneritic.
Granite and rhyolite are similar in that they have the same mineralchemical composition. As a result they form sprawling and diverse towers over many hundreds of miles. A batholith from Greek bathos depth lithos rock is a large emplacement of igneous intrusive also called plutonic rock that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earths crust.
During the Jurassic era 150 million years ago an island arc. Batholiths may form areas of high land as the material around them is removed by weathering and erosion. Therefore granite has a phaneritic texture while rhyolite is formed extrusively and so has an aphanitic texture.
Although they may appear uniform batholiths. So batholith is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock that can be as large as 100 square km. They are different in that granite forms when magma cools intrusively.
This batholith forms the core of the Sierra Nevada mountain range. Batholiths are large areas of intrusive usually granitic rock typically associated with subduction zones or hot spots. Due to intrusive volcano activity intrusive igneous rock formation occurs here.
Batholiths are large bodies of intrusive igneous rock. Identify and explain two possible mechanisms that can. Formed when magma cools and crystallizes beneath Earth s surface batholiths are the largest type of pluton.
They appear on the surface only after the denudation processes remove the overlying materials. Thus they form simultaneously within mountain ranges. These penetrate up through the ground and cause plutons and explosive cone volcanoes as shown in the diagram.
And that gneissic terranes form. They have a planar base but a domed upper surface above which the country rocks are arched up. They are formed from the hot magma that penetrates into other rocks below the Earths surface.
Some of these sediments are partially subducted but the dissolved water lowers their melting point so they form a molten mass called a batholith. Synthesizing plans uh they consumed CO two and form 02 Thus creating an oxidizing environment for in the results of this is that many transition metals are now in the form of metal oxides.
Intrusive Igneous Activity Ppt Video Online Download

Batholith Geology Characteristics Formation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
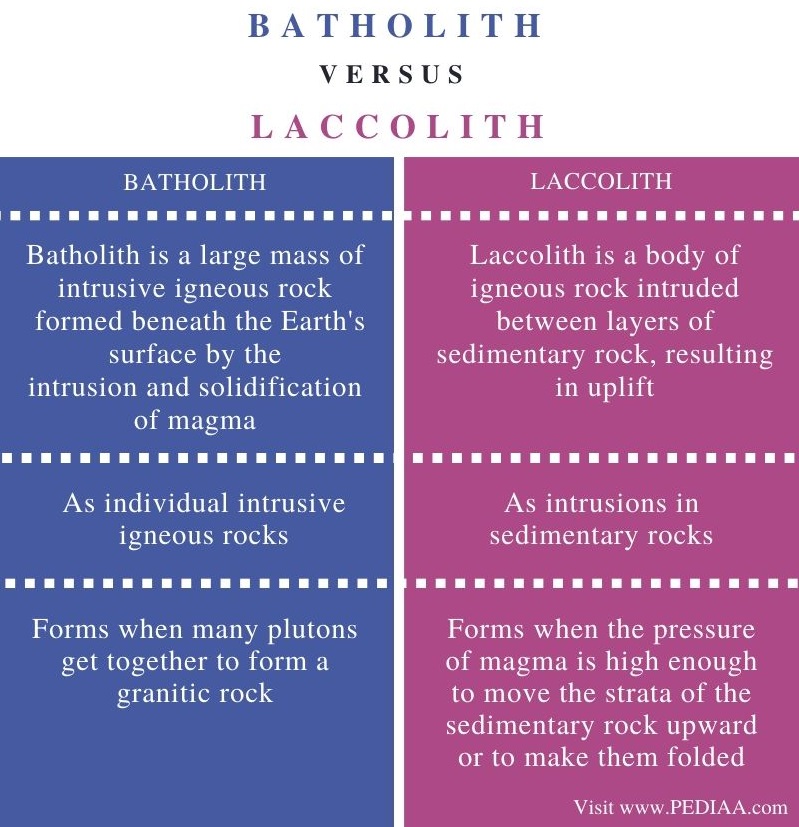
What Is The Difference Between Batholith And Laccolith Pediaa Com
No comments for "Describe Batholiths and Explain Where and How They Form"
Post a Comment